Oude Meer, the Netherlands (March 2022) — The Ushio Group (Head Office: Tokyo; President and CEO: Koji Naito; subsequently referred to as “Ushio”) is expanding its “chip-only” product line to cater for other packaged LED manufacturers and those who seek more flexibility in their product design. Already established in the solid-state lighting (SSL) field with its own packaged LED and laser diode products, Ushio has announced its entry into the bare SWIR LED chip market. This move is expected to catch the attention of companies producing LEDs with a reduced mounting area and compact device OEMs in the smartphone and vital sensor industries.
Realizing the “world’s most efficient SWIR LEDs” with technological advancements
Following a complete redesign of its existing Epitex S Series, Ushio Inc.’s Epitex D Series short-wavelength infrared (SWIR) LED chips offer a significant leap in efficiency thanks to the introduction of new LED device structural technology. The new D Series presents some attractive improvements that will be sure to catch the eye of manufacturers who seek to package the LED chips themselves or require design flexibility. Industries that will benefit from the new design include manufacturers of smartphones & mobile devices, vital signs monitors, and proximity sensors.
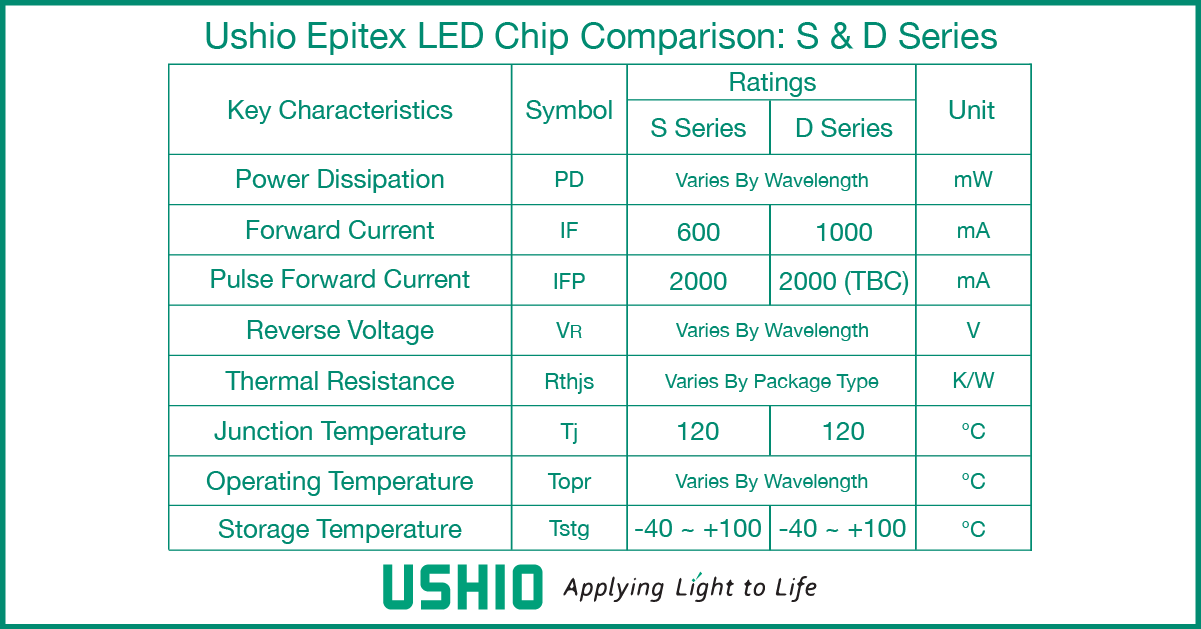
Technical improvements of Epitex D Series SWIR LED chips
Improved heat dissipation and higher LED radiance by InP substrate lift-off process
Ushio had previously identified indium phosphide (InP) as its preferred substrate for epitaxial growth; however, the skilled engineers were keen to improve the relatively low thermal conductivity. Assigned the task of improving heat dissipation, the Ushio LED division looked for a way to achieve higher thermal conductivity.
The Japan-based team established a mass production process, termed “InP substrate lift-off”, in which the InP substrate is replaced by a support substrate with high thermal conductivity. Due to temperature rise, InP sees a relatively large drop-off in efficiency, so this improvement in heat dissipation has improved the overall efficiency under actual use conditions.
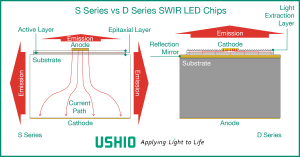
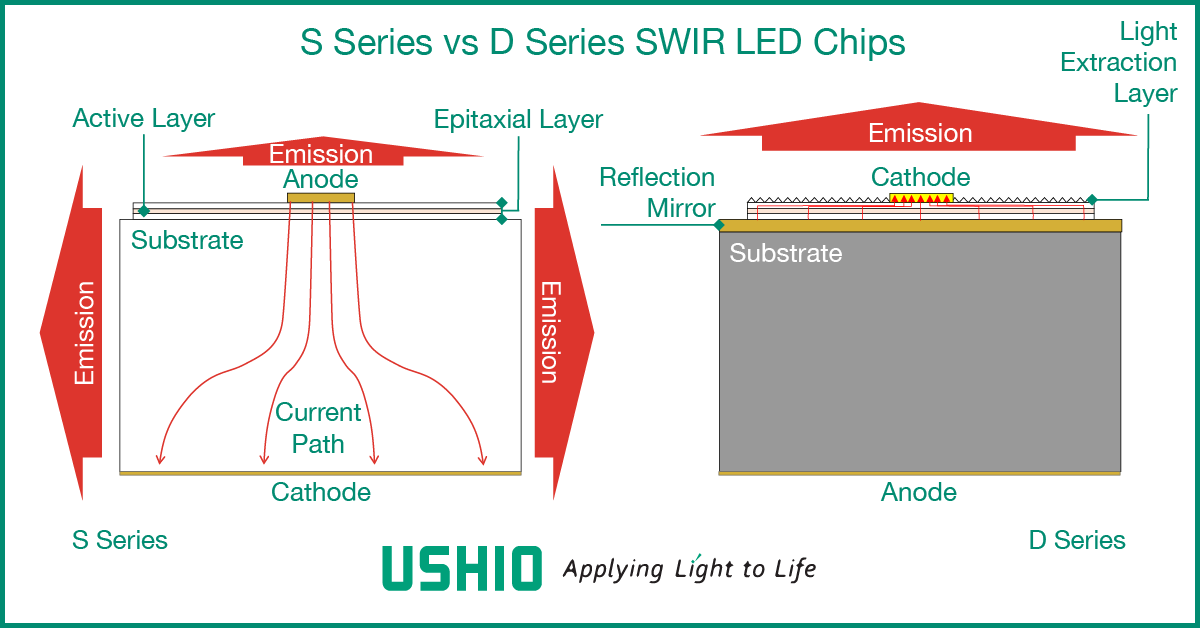
Since the InP substrate transmits SWIR light, the light emitted from the active layer of conventional SWIR LEDs (Ushio Epitex S Series) is extracted not only from the epitaxial layer but also from the side of the substrate. As a result, the spread of the emitted light is greatly dispersed.
In contrast, in the structure of Ushio’s newer Epitex D Series, the InP substrate is removed and a highly reflective layer is placed between the support substrate and the epitaxial layer. In order to form a highly reflective layer, the materials and structure of the reflective layer were carefully studied so as not to cause an increase in the electrical resistance inside the LED, and both electrical and optical characteristics were achieved.
As a result, light is extracted only from the thin epitaxial layer, and LED radiance is improved. For optical designers, a light source with high radiance is generally easier to design and use in optical systems.
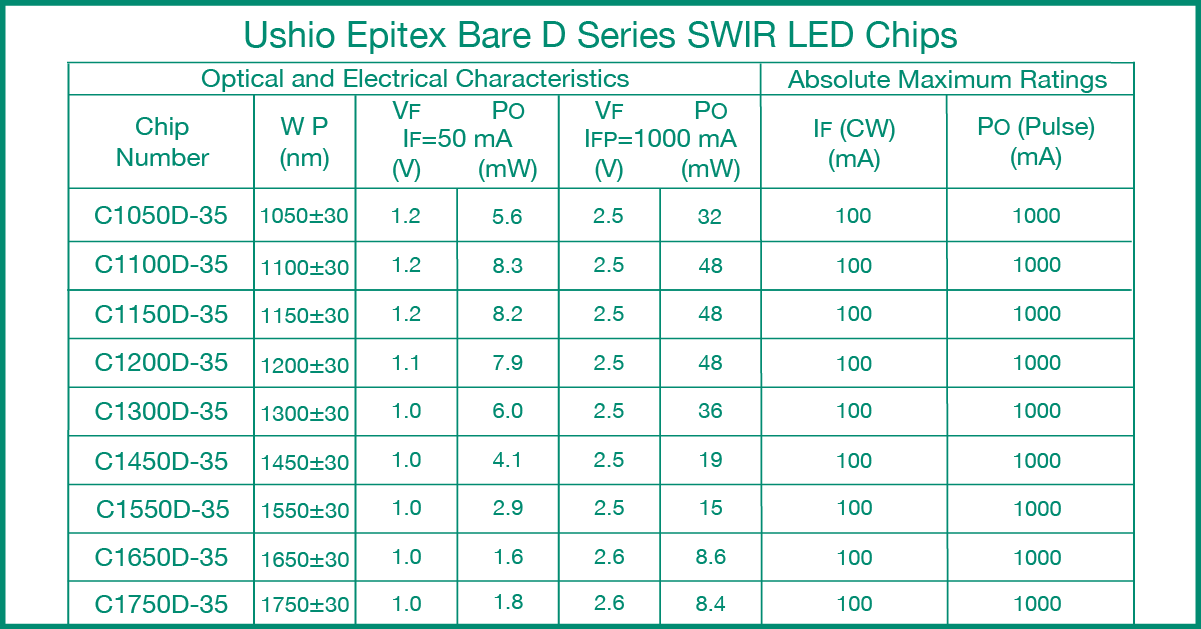
Light out-coupling efficiency improved with new extraction structure on chip surface
In order to realize high LED efficiency, light must be extracted from the active layer to the outside of the semiconductor crystal efficiently; however, it is difficult to extract light from a crystal with a high refractive index, because total reflection occurs at the interface between the semiconductor and air.
If the surface of the device consists of a flat plane, only a few percent of the light emitted inside the crystal can be extracted to the outside; furthermore, the light trapped inside the crystal is eventually absorbed as it is repeatedly reflected inside the crystal. Ushio has improved these characteristics by the following methods.
The formation of a rough structure on the chip surface, in order to suppress the total reflection at the chip-air interface, improves the light extraction efficiency of LEDs. The rough structure is formed on the LED surface by a new and intricate etching process. This unique method of forming homogenous surface irregularities has been shown to improve the light out-coupling efficiency, while a highly reflective mirror reduces light loss inside the chip to maximize the efficiency of light extraction.
Higher efficiency and reliability with internal chip current path control
In many LEDs, the resistance of the area directly under the electrodes is low, so the current tends to be concentrated there. Since LED light emission is usually proportional to the amount of current running through it, the amount of light emitted directly below the electrodes increases when current is concentrated there. This gives rise to a problem, in that the light emitted directly under the electrode is shadowed by the electrode, and the light cannot be sufficiently extracted from the crystal. At the same time, current concentration causes a local stress on the crystal, which is undesirable for the reliability of the device.
Ushio’s engineers investigated new design possibilities, in regards to the electrode arrangement and shape, to facilitate the spread of current inside the crystal. These improvements suppressed the luminescence just below the electrodes and increased the effective light. As a result, the current concentration was suppressed and the reliability was improved under higher driving currents.
Contact Ushio about Epitex D Series SWIR LED chips
If you would like to make an enquiry regarding the suitability of Ushio’s Epitex D Series SWIR LED chips for your project, please contact us here.
Further Reading
Ushio Europe Solid State Lighting Hub (News, Technical Information, and more)