Excimer Lamps & Modules

For surface pre-treatment and disinfection purposes
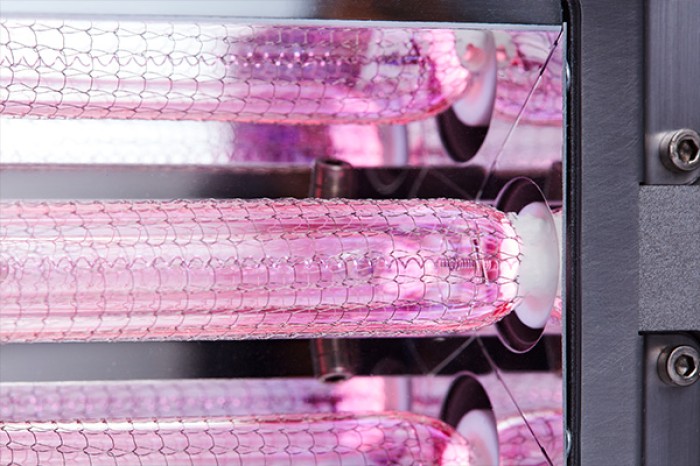
Excimer lamps are specially coated, noble gas-filled emitters that emit a desired vacuum ultraviolet (VUV) wavelength, depending on the combination of noble gases used to fill the sealed quartz glass chamber.
In particular, Ushio offers two wavelengths of excimer lamps and modules: 172 nm and 222 nm. The 172 nm wavelength is most commonly used in industrial surface pre-treatment applications. 222 nm far-UV-C excimer lamps have been gaining in importance for some time due to their ability to thoroughly disinfect surfaces and air.